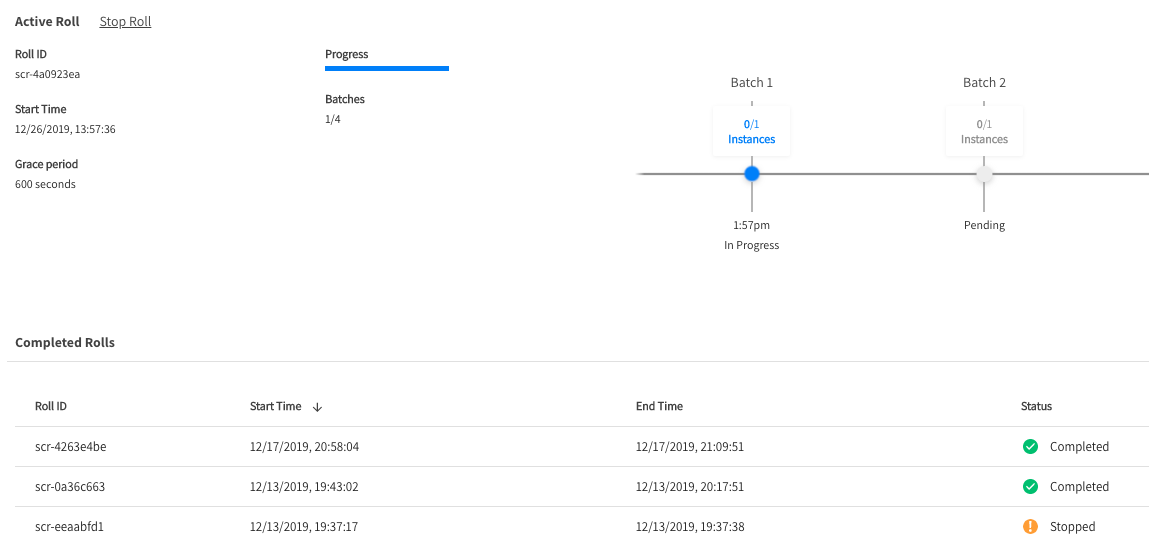
Rolls
Cloud service provider relevance: AWS Kubernetes, AWS ECS, GKE.
For AKS, see AKS Roll.
The Roll feature lets you perform changes to align cluster infrastructure with a new image, user data, or security groups without turning off the Ocean autoscaler or manually detaching nodes in the cluster.
This topic uses Kubernetes terms such as node and pod. The ECS and AKS equivalents such as container instance or VM and task are also applicable.
In Ocean, you can roll your cluster with a single click. The roll considers the actual workloads running in the cluster. Ocean freezes scale-down activity in the cluster and launches new compute capacity to match the workload requirements. While the new nodes are starting up, the old ones can still scale up if necessary and will scale down only after the new ones are healthy.
How It Works
Whether you are rolling your entire Ocean cluster, a specific virtual node group (VNG), or only specific nodes, Ocean can divide the roll into batches according to your selected batch sizes. For example, if you roll with the default batch size of 20%, Ocean divides the roll into 5 batches and processes as follows:
-
Ocean calculates the number of batches required based on your specified batch size and distributes workloads evenly across the batches.
-
Ocean begins with the first batch, replacing each node while ensuring workloads are successfully accommodated on new nodes. All relevant constraints are considered during the replacement process.
-
When all nodes in a batch finish processing and at least 50% are successfully replaced, Ocean proceeds to the next batch. You can configure this percentage using the
batchMinHealthyPercentageparameter (described later).
Replace Node with Smaller Nodes
A cluster roll can replace a single node with multiple smaller nodes. This avoids a cluster roll failure when only smaller node types are configured in the Ocean cluster before initiating the roll. Rather than replacing each existing node with one of the same type, Ocean provisions the most relevant infrastructure during the cluster roll. This is based on the workloads currently running on the nodes selected for rolling. This is especially helpful when you have modified the list of allowed node types or if you want to remove and replace a specific node type with multiple smaller ones.
This approach can improve cluster utilization by running workloads on infrastructure that better matches their requirements. While Ocean constantly attempts to scale down the cluster, a cluster roll can achieve better utilization when automatic scaling is not possible.
Respect Pod Disruption Budget
Some pods may have a pod disruption budget (PDB). Use the respectPdb parameter to have Ocean check the PDB. When respectPdb is set to True, Ocean will not replace a node if the PDB is violated.
Minimum Healthy Instances in Batch
The batchMinHealthyPercentage parameter indicates the minimum required percentage of healthy instances in a batch. The cluster roll will fail if the amount of healthy instances in a single batch is under this percentage. The range is 1-100. If the value is null, the default value 50% applies. Instances that were not replaced due to PDB will be considered as healthy. You can override this behavior by setting ignorePdb to True.
Node Status
During the replacement process, Ocean reports a status for each node:
-
REPLACED: The node was successfully replaced with a new node.
-
TO_BE_REPLACED: Ocean has not yet attempted to replace this node.
-
COULD_NOT_BE_REPLACED: The node replacement failed. This typically occurs when no replacement node becomes healthy within the grace period.
-
NOT_REPLACED_DUE_TO_PDB: Node replacement would violate the PDB configuration for one or more pods running on the node. This status only applies when
respectPdbis set toTrue. Nodes with this status are considered successfully replaced for batch progression purposes. If all nodes in a batch receive this status, Ocean will proceed to the next batch even if no actual replacements occurred.
Roll Status
Ocean assigns a status to each stage of the roll process. A roll can have one of these statuses:
-
IN_PROGRESS: The roll remains in this status while nodes are being successfully replaced.
-
FAILED: An error occurred that caused the roll to fail. The error message is recorded in the Elastilog.
-
STOPPED: The user manually stopped the roll. Nodes retain their current state when stopped, with no rollback to the initial configuration.
-
COMPLETED: The roll reaches this status when all nodes have been processed and at least 50% have been successfully replaced.
In the UI console, a specific batch may appear with a Pending state. This means that even though the roll process has started, that batch has not yet started to replace its nodes.
Log Messages
The following messages are recorded in the log:
Roll $\{ROLL_ID} has completed successfully.Roll $\{ROLL_ID} has failed. Reason: $\{FAILURE_REASON}.Roll $\{ROLL_ID} has started. Number of batches $\{NUM_OF_BATCHES}.Roll $\{ROLL_ID} has stopped.
The following are possible reasons for failure:
- The roll has been stuck in the same roll status for too long.
- The Ocean Controller is not active.
- More than 50 percent of nodes could not be replaced.
- There may be constraint mismatches or configuration mismatches such as labels, selectors, taints, or affinity rules.
- There may be one or more unhealthy nodes.
Restrict Scale Down during Roll
The roll does not consider the restrict-scale-down label. Ocean will replace a node even if a task or pod uses this label. The Ocean autoscaler considers all relevant constraints in place before the roll.
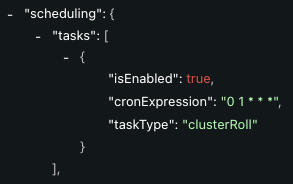
Schedule Cluster Roll
You can schedule a roll in the Spot API under Create Cluster or Update Cluster using a cron expression. Set it to roll during off-hours.
Roll per Node or VNG
Ocean virtual node groups (VNGs) let you run different node groups within a single Ocean cluster. This way, you can run different groups of nodes on the same cluster, so that for example:
- Separate development, test, and production environments
- Different teams
- Different applications or microservices
If you don't need to roll the entire cluster, such as for a local software update, you can specify a list of node IDs or a specific virtual node group ID.
Example:
- Use the
instanceIdsparameter (Ocean for Kubernetes on AWS and ECS) orinstanceNames(Ocean GKE) to initiate a roll of one or more specific nodes. - The
launchSpecIdsparameter initiates a roll of one or more virtual node groups in the cluster. When you specify a virtual node group ID, all the nodes in that virtual node group are rolled.
For more information about the specific APIs, see Initiate Cluster Roll: Kubernetes on AWS, ECS, GKE
Start A Cluster Roll
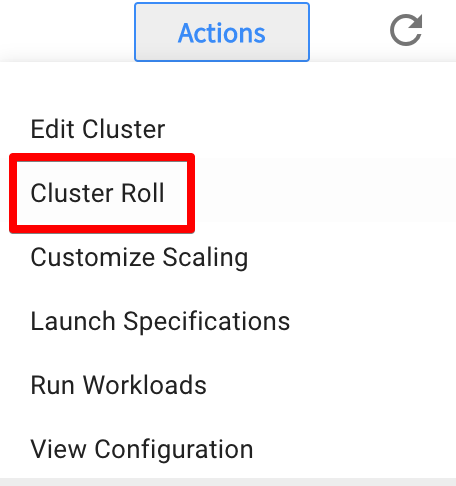
-
In your Ocean cluster, go to Actions and click Cluster Roll.
-
Enter the following information:
- Batch Size: Indicates how much will be rolled at a time. This value is a percentage of the cluster's target capacity.
- Comment: Describe the reason for the roll.
- Respect Pod Disruption Budget: Accept the default setting, or uncheck if you do not want to respect the PDB.
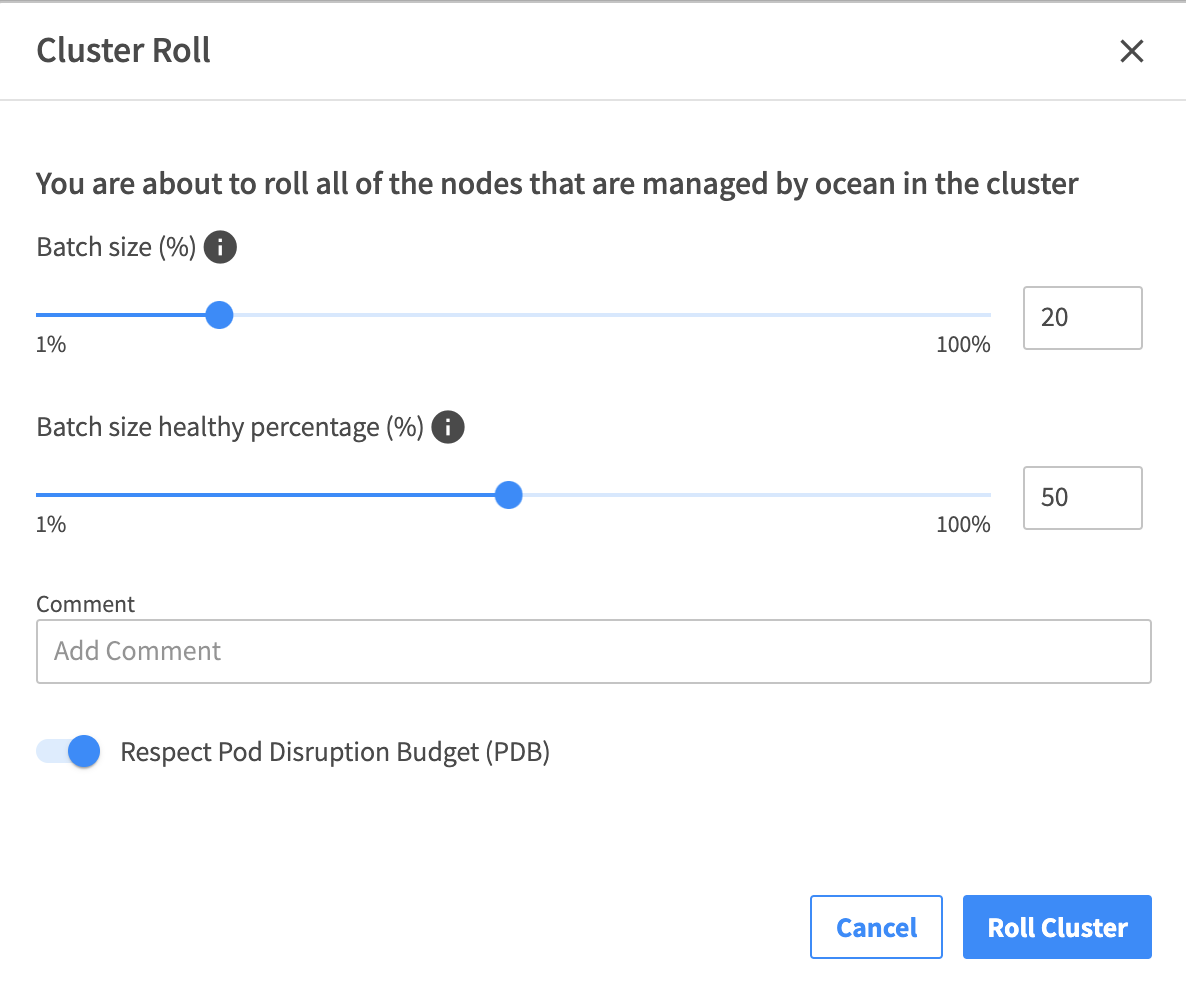
-
Click Roll.
Start a VNG Roll
-
In your Ocean cluster, click the Virtual Node Groups tab.
-
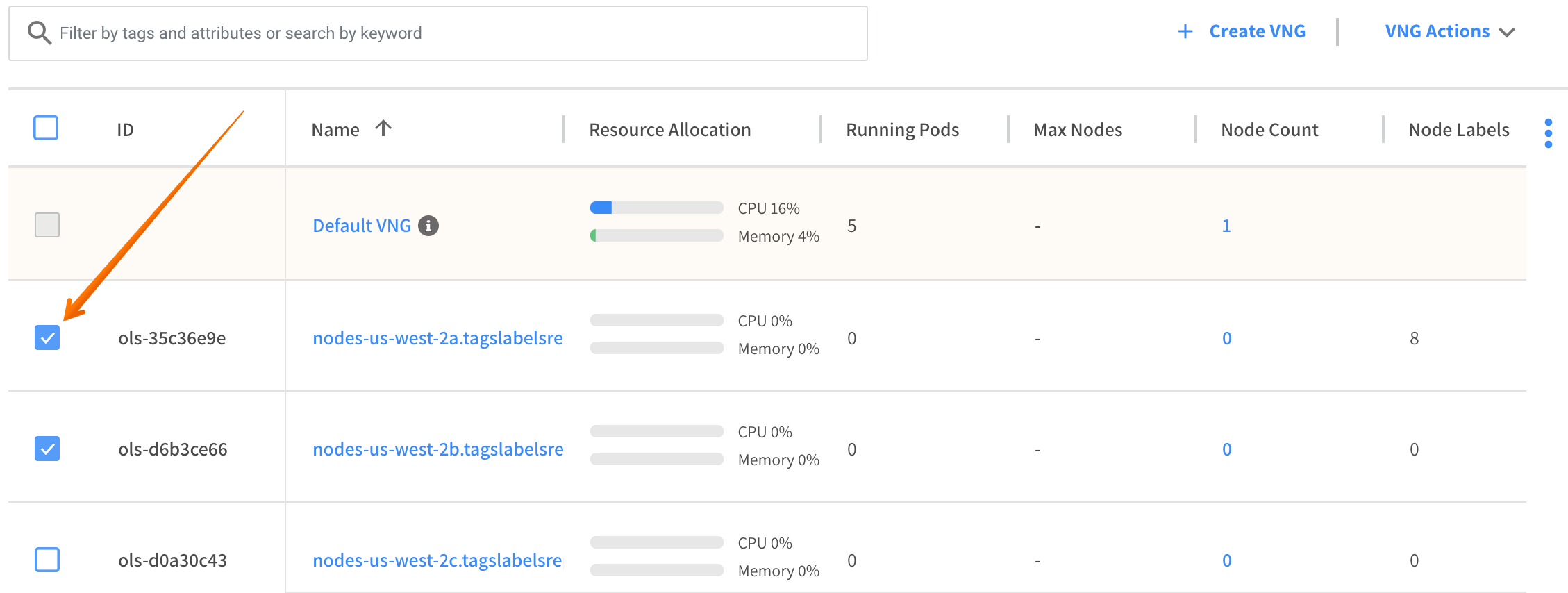
Select checkboxes for the virtual node groups to roll from the list.
-
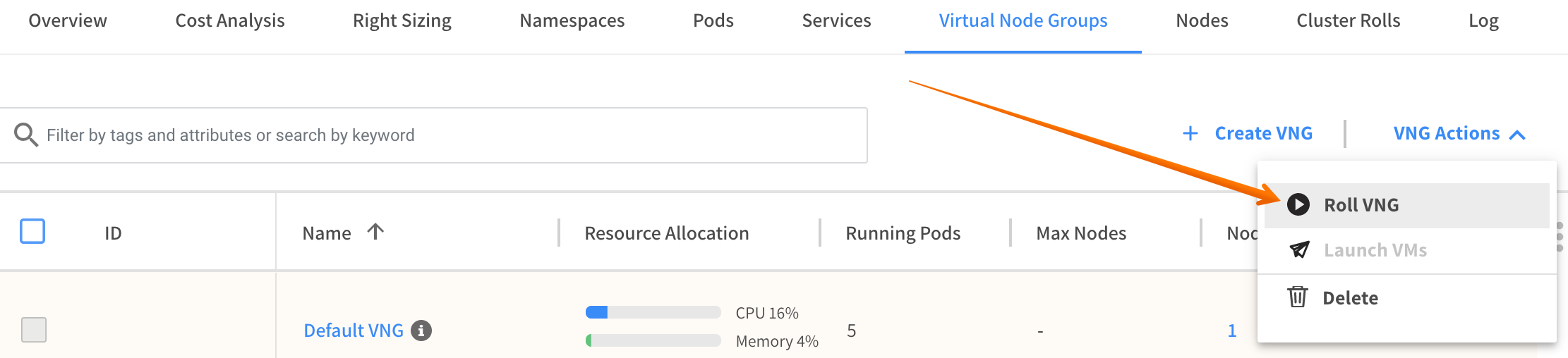
Click VNG Actions and Roll VNG.
-
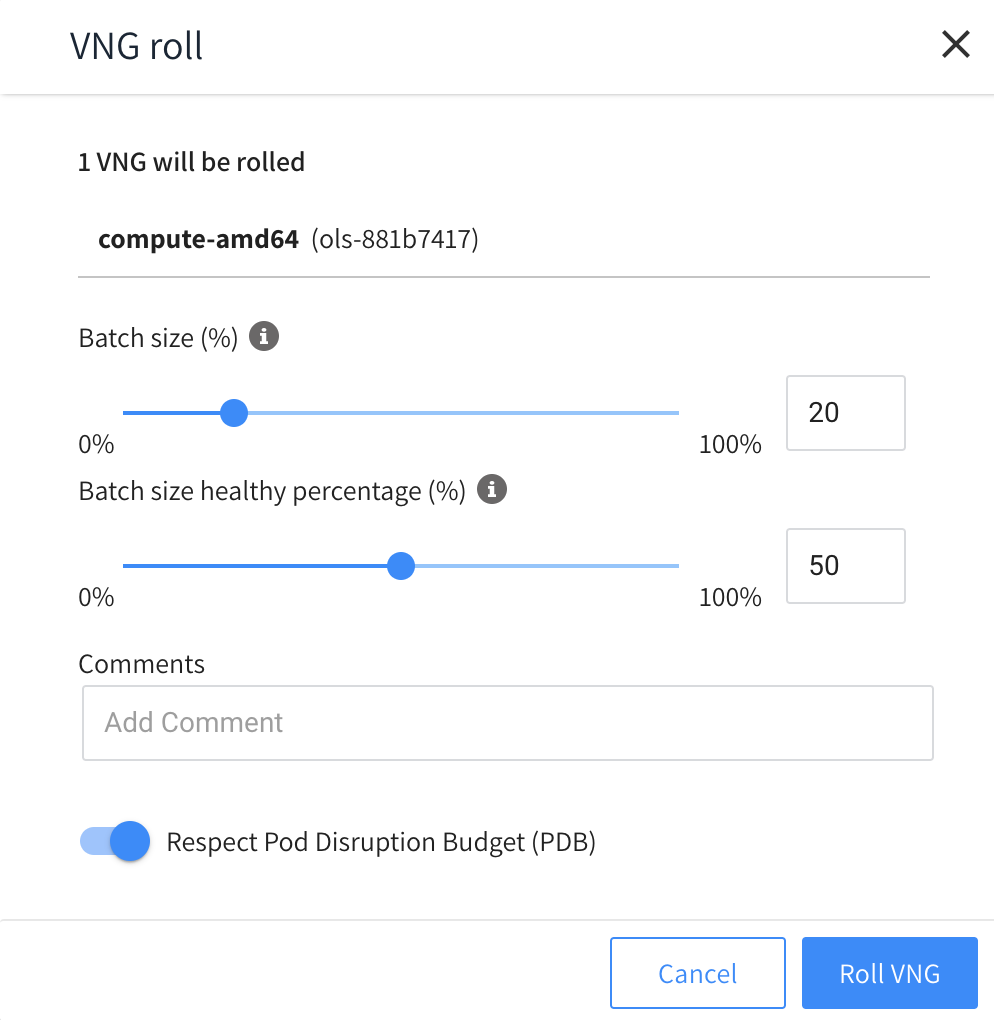
Enter the Batch Size and Comments, indicate whether you want to respect the pod disruption budget, and click Roll VNG(s).
Monitor The Roll
After you have created the roll, click the Cluster Roll tab.
View the roll details and follow the progress.